Where is the pancreas? It lies partially behind your stomach, with the other part being is nestled in the curve of your small intestine (duodenum). It is in between your spine and stomach. It is buried deep and is non palpable. Hold your thumb to your little finger of your right hand, keep the other three fingers straight and upright, and then place your hand in the center of your tummy right below your lower rib, pointing the three fingers left. This is about where it is.
The parts of the pancreas are
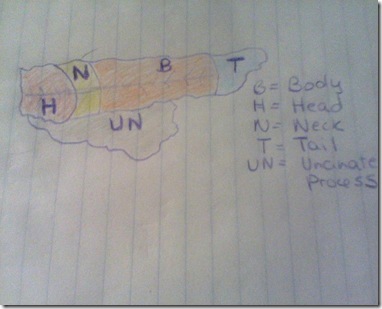
The pancreas is composed of a system of ducts and glandular tissue. The Pancreatic duct is the main duct and runs the length of the pancreas. It drains the pancreatic fluid from the glad and carries it to the duodenum/small interesting. This main duct has many small side branches and itself is only about 1/16 of an inch. The pancreatic duct joins with the bile duct to form the ampulla of Vater. This a widening of the duct right before it enters the duodenum/small intestine.
We can think of the pancreas as having different functional components, the exocrine and the endocrine parts. The Islets of Langerhan are the endocrine (endo=within) cells of the pancreas secrete and produce hormones into the bloodstream. Insulin and glucagon, the pancreatic hormones, work together to keep the levels of sugar in the blood at proper levels. This sugar, called glucose, is used for energy by the body.
Acinar cells are the exocrine (exo=outward) cells that produce and transport enzymes that will leave the body through the digestive system. They are secreted in the duodenum/small intestine where they help in the digestion of food.
So the pancreas is an integral part of the digestive system. When the pancreas is functioning normally, when food is eaten the glucose and amino acids trigger the pancreas to secrete insulin. The insulin binds to cells and opens the pathway of the cell to open letting glucose, amino acids, nutrients and fats to enter. The cells then begins a process of converting these nutrients into energy. After these nutrients are cleared from the blood the pancreas stops producing insulin. Cells are covered in insulin receptors. These receptors can become resistant and create a condition known as Insulin Resistance. When the insulin can’t get glucose and nutrients into the cells the blood glucose levels remain high and the pancreas produces even more insulin. It is a vicious circle then. The blood stream is saturated with glucose, but insulin levels continue to rise and nutrients can not nourish the cells.
Profile of Insulin Resistance
Elevate triglycerides (>150) or depressed HDL cholesterol (<40 male <50 female)
Waist:hip ratio> or equal to 1 in a male, or waist >40
Waist: hip ratio > or equal to 0.8 in a female, or waist > 35
Abnormal glucose tolerance// Fasting glucose > 10
Why do people become Insulin Resistant?
Genetics (25% of cases)
A diet high in simple carbohydrates with a lack of protein
Lack of resistance exercise
Lack of Essential Fatty Acids
Lack of specific nutrients and trace elements
Too much stress
Lack of sleep
Insulin Resistance can cause difficulties loosing weight, increase your risk of some types of cancer, cause obesity, high cholesterol, hypertension,thrombosis, atherosclerosis, osteoporosis, hypothyroid, and increase risk of diabetes.
The cells in the liver are the first cells to become insulin resistant. The liver normally stores glucose in the form of glycogen. In Insulin Resistance, the liver doesn’t sense the presence of glucose and starts making more. This process is known as gluconeogenesis. This liver formed glucose is sent into the blood stream making the already high level of blood sugar, even higher. The liver then stops breaking down fatty acids and starts storing them instead.
White adipose tissue (WAT) is used for storing retrievable fat for energy around the abdomen. This WAT secretes Leptin, a hormone, which sends a signal to the hypothalamus in the brain, telling it that the fat cells are full and it is time to burn some. When the Leptin levels rise the pancreas is also signaled to stop secreting insulin. Leptin is secreted when insulin is binding to cells or when fat cells are full. But, when the levels of glucose and insulin in the bloodstream are high and there is an excess of fat around the abdomen there is a disruption in the the Leptin signal and Leptin levels begin to rise. This high levels of Leptin causes the pancreas and hypothalamus to become defensive and reduce the number of Leptin receptors. This condition is called Leptin resistance. With this disruption of the Leptin signals the person always feels hungry and the metabolism slows down fat burning. The pancreas secretes more insulin and the cycle continues.
The stomach walls secrete a hormone called Ghrelin. This hormone functions to send a signal to stimulate appetite when the stomach is empty. Growth hormone, which builds muscle, burn fat and to sensitize insulin resistant cells is also secreted in response to Ghrelin. But, in Insulin Resistance, the high levels of insulin and glucose disrupt the signal. The insulin levels continue to rise and Growth Hormone secretion is lessened. This having all these disrupted signals cause us to think we are hungry, even when we have eaten, and contributes to weight gain and not lean muscle building.
High levels of insulin promotes fibrinogen. This increases blood clotting and decreases PAI-1 which inhibits clot breakdown. Both of these factors greatly increase the risk of thrombosis, strokes and heart attacks.
Stress, lack of sleep and lack of exercise can contribute to Insulin Resistance. The adrenal glands secrete the hormone cortisol in response to stress on the body. When cortisol is release due to stress the liver secretes glucose as a form of energy. The glucose signals the pancreas to release insulin. When stress is prolonged the cycle continues and leads to Insulin Resistance. If a person is pre-diabetic, this presence of cortisol can cause diabetes. The cycle of high levels of insulin and cortisol can lead to adrenal exhaustion.
A person can develop hypothyroid, underactive thyroid, when blood levels of insulin are high. The thyroid hormones are less able to convert T-4 to T-3 hormones.
When bone cells become insulin resistant Osteoporosis is likely to occur. Insulin helps protect bones and breaking down and promotes collagen formation.
Growth hormone helps build lean muscle, burn fat and increases insulin sensitivity. Exercise increases the production of growth hormone. Insulin suppresses Growth hormone.
This Insulin Resistance, is also called Metabolic Syndrome, or Syndrome X. Herbalist Paul Bergner suggests this treatment. All three suggestions must be done simultaneously
Supplements the nutritional deficiencies:
60mg Zinc
800 mg magnesium
600-800 mcg chromium
B-100 complex- complete
Lots of antioxidants: Vitamin C, E, etc
L-carnitine, 500 – 4000 mg
Eat a low carbohydrate diet
Fish oil and flax oil while restricting others. Regular fish consumption is recommended.
Most days do a minimum of 15-20 minutes of resistance type exercise. Exercise that reaches the anaerobic phase.
Don’t smoke
Consult your physician before starting any diet or exercise program
Herbs that might be beneficial include fenugreek, cinnamon, Maitake mushroom and coffee
Herbal and Honey Hugs to all who visit Comfrey Cottages xx
sources: Paul Bergner’s writing and John Hopkins University website










1 comment:
Get of gluten grains and dairy and you should see an improvement, check out the book dangerous grains
Post a Comment